
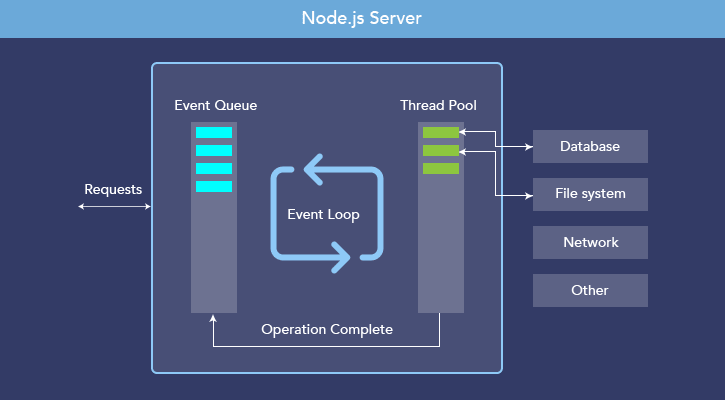
The request object captures all the data of the HTTP request that’s coming in. This function must have two arguments, a request object and a response object. This function is meant to handle an incoming HTTP request and return an HTTP response. Let’s add a special function, which in Node.js we call a request listener. When we bind our server to this host and port, we will be able to reach our server by visiting in a local browser. Ports 80 are typically used as default ports in development, and in most cases developers will use them rather than other ports for HTTP servers. In our example, we will use port 8000 for our web server. The port is a number that servers use as an endpoint or “door” to our IP address. It’s typically the equivalent of the internal IP address 127.0.0.1 and it’s only available to the local computer, not to any local networks we’ve joined or to the internet. The value localhost is a special private address that computers use to refer to themselves. For more information on domain name concepts, take a look at our An Introduction to DNS Terminology, Components, and Concepts article. An IP address is a unique sequence of numbers that identify a machine on a network, like the internet. We may interact with a web server by entering a domain name, which is translated to an IP address by a DNS server. const host = 'localhost' const port = 8000 Īs mentioned before, web servers accept requests from browsers and other clients. Add the following line to hello.js:įirst-servers/hello.js. We start by loading the http module that’s standard with all Node.js installations. We will use nano as it’s available in the terminal: Now, create the file that will house the code: In the terminal, create a folder called first-servers: This will cover the key concepts required to set up a server, which will provide the foundation necessary to return more complex data formats like JSON.įirst, we need to set up an accessible coding environment to do our exercises, as well as the others in the article. Let’s start by creating a server that returns plain text to the user.
#Quick node web server how to
If you’re not familiar with asynchronous programming in Node.js or the fs module for interacting with files, you can learn more with our article on How To Write Asynchronous Code in Node.js.
#Quick node web server install
To install this on macOS or Ubuntu 18.04, follow the steps in How to Install Node.js and Create a Local Development Environment on macOS or the Installing Using a PPA section of How To Install Node.js on Ubuntu 18.04. This tutorial uses Node.js version 10.19.0.

#Quick node web server software
This software generally falls into two categories: frontend and backend. A web server receives HTTP requests from a client, like your browser, and provides an HTTP response, like an HTML page or JSON from an API.Ī lot of software is involved for a server to return a webpage. That computer you are talking to via the internet is a web server. When you view a webpage in your browser, you are making a request to another computer on the internet, which then provides you the webpage as a response. The author selected the COVID-19 Relief Fund to receive a donation as part of the Write for DOnations program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
